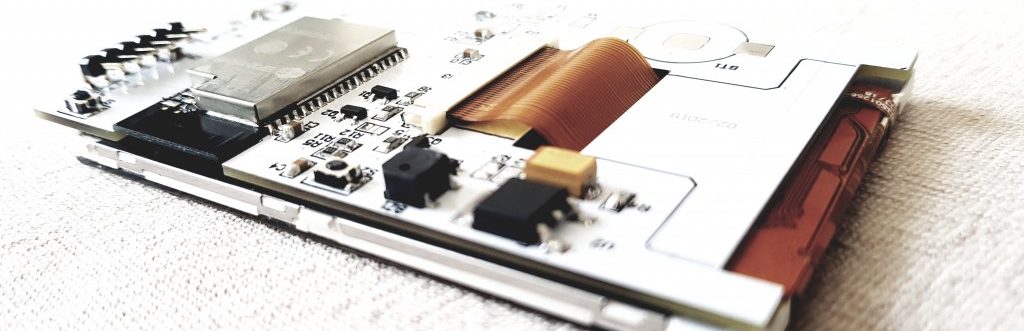
Few weeks ago I decided to teach myself Eagle PCB so I can put my current spaghetti-style solution for heat pump monitoring to some order. That’s just an excuse of course, I was curious how laying out a new PCB works to begin with. Since my current solution is based on the EmonTX, I decided to continue that and design an Arduino shield with the same function. So why a shield? Well because I do have couple Arduinos around and I’d like to use them. Also the NaNode’s ENC28J60 ethernet chip has been quite a challenge with the single packet TCP implementation in the MCU’s RAM, so I felt it would be nice to diversify the hardware platforms for a change. I am planning to use an Arduino Ethernet board with the newly designed shield, but it may also be used on a NaNode v5 or NaNode RF (by not soldering the RFM12B module on the shield).
So here are the designs I came to:
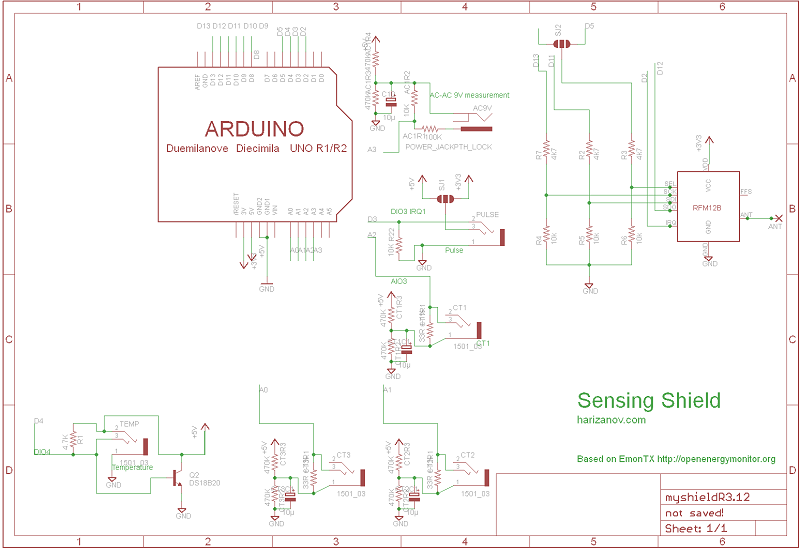
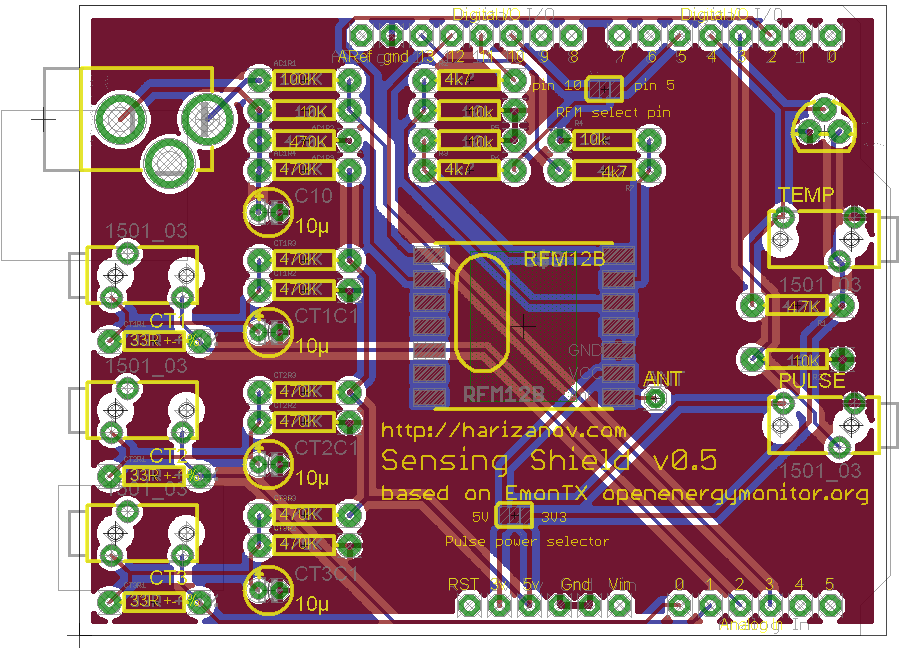
The Eagle schematic and board files are here.
The shield has
- Three inputs for Current Transformers with 2.5mm audio jacks
- One input for 9V AC/AC transformer input for measuring voltage
- One input for pulse output devices (like flow sensor); Voltage selector solder jumper allows powering that port with 3.3V or 5V
- One input bus for DS18B20 digital temperature sensors
- On-board socket for DS18B20 for room temperature measurement
- RFM12B radio module for remote wireless sensors; Solder jumper allows usinf DIG5 or DIG10 for SPI select
edit: The Sensing Shield is now available for sale in the store
Pingback: Using the Sensing Shield for logging solar hot water tank temperatures to Pachube | Martin's corner on the web
Pingback: Martin's corner on the web